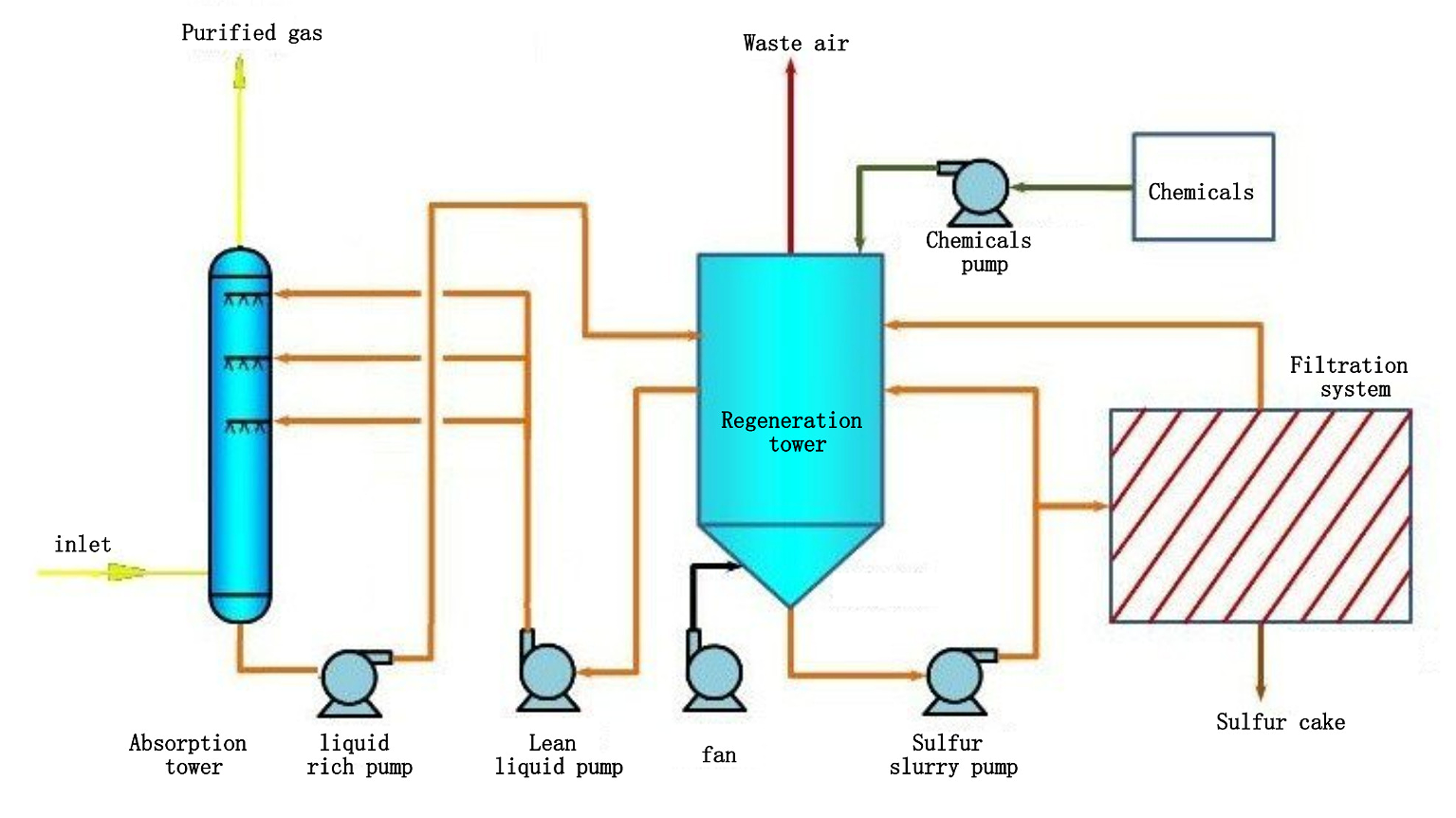
Working Principle
The aqueous solution absorbs H2S gas and the ferric ions (Fe3+) oxidize divalent sulfur. The total absorption and oxidation reaction equation is H2S(g) + 2Fe3+(L) → 2H+(L) + S↓+ 2Fe2+(L).
The complex ferrous ion solution is directly contacted with the air for gas-liquid reaction, then the oxygen in the air is used to oxidize the complex ferrous ions in the aqueous solution into complex ferric ions. The regeneration reduction reaction equation is
1/2O2(g) + H2O(L) + 2Fe2+(L) → 2OH-(L) + 2Fe3+(L).
The iron ions are not consumed in the reaction. The iron ions serve as the catalyst for the reaction of hydrogen sulfide and oxygen.
Since the treated gas phase contains carbon dioxide (CO2), especially at high pressure, carbon dioxide is very soluble in water and will form bicarbonate (HCO3-) and carbonate (CO32-), followed by a side reaction to reduce the pH value of the aqueous solution. In order to stabilize the pH value of the aqueous solution, sodium hydroxide needs to be added to the system.
The system uses the redox properties of the alkaline complex iron catalyst to absorb H2S in the acidic gas. H2S is directly oxidized by the complex iron to generate elemental sulfur, and the complex iron is converted into complex ferrous iron. Then air is blown into the regeneration sedimentation tank to oxidize the complex ferrous iron in the alkaline absorbent, so that the complex ferrous iron in the absorbent is converted into complex iron for regeneration and reuse. At the same time, the sulfur is precipitated and separated in the regeneration sedimentation tank to form sulfur slurry, and the sulfur slurry is sent to the filter to be dehydrated into sulfur cakes.
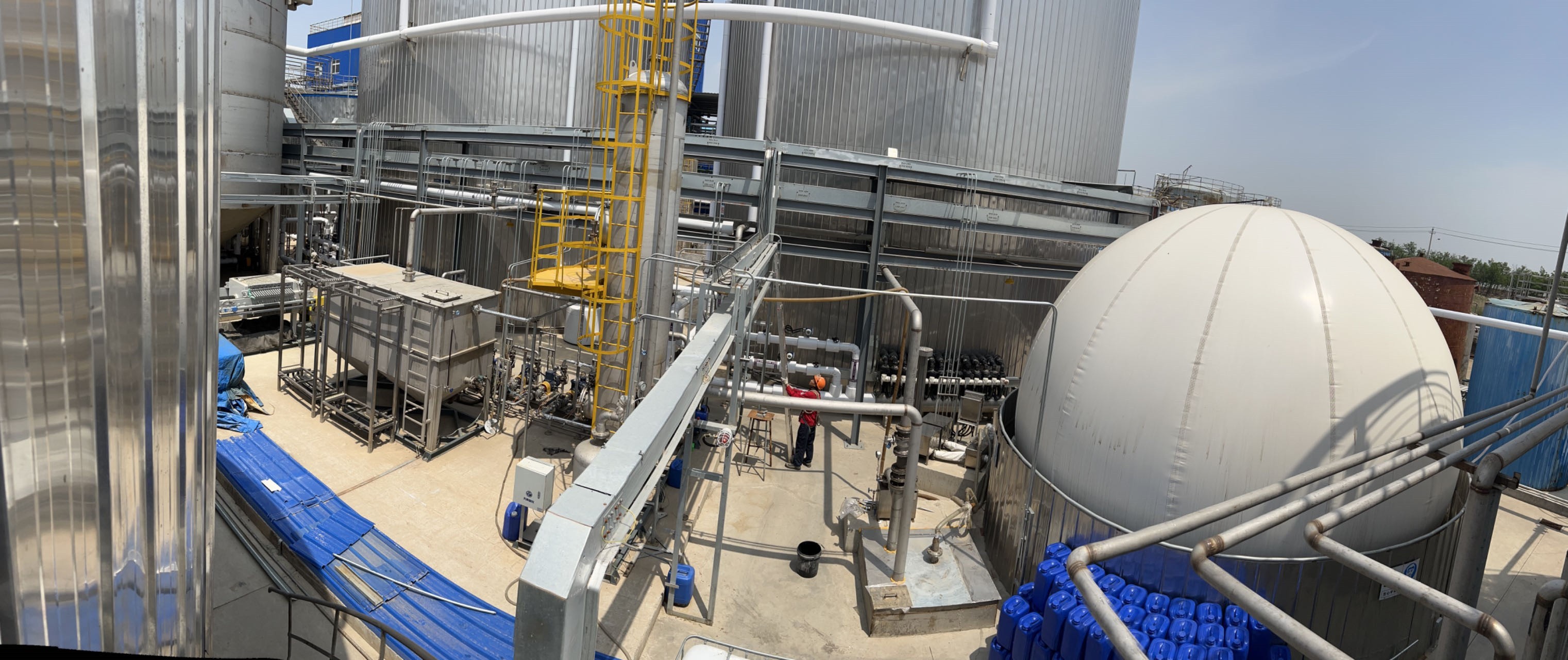
Treatment Process